Dark Gums
Dark Gums A beautiful smile is often associated with pearly white teeth, but what about the color of the gums? While gum health is crucial for maintaining oral hygiene, the aesthetic aspect of gum color should not be overlooked. Dark gums, although a natural variation, can sometimes cause self-consciousness.
Introduction:
Dark Gums and concern for individuals. In this article, we delve into the causes behind dark gums, explore possible remedies, and shed light on cultural perspectives surrounding this phenomenon.
Understanding Dark Gums:
Dark gums, also known as hyperpigmented gums, refer to the presence of darker color in the gum tissue compared to the standard pinkish hue. This condition is relatively common and can affect individuals of all ethnic backgrounds. The color of our gums is primarily determined by melanin, the pigment responsible for the color of our skin, hair, and eyes. When an excess of melanin is produced or deposited in the gums, they can appear darker.
Causes of Dark Gums:
-
Ethnicity and Genetics: Darker gum color is more prevalent in individuals with higher levels of melanin. People with African, Asian, or Native American ancestry tend to have higher melanin concentrations in their gums, resulting in naturally darker gum tissue.
-
Smoking: Tobacco use, whether through smoking or chewing, can contribute to the darkening of the gums. The harmful chemicals in tobacco can cause melanin to accumulate and discolor the gum tissue over time.
-
Medications and Hormonal Changes: Certain medications, such as minocycline, antimalarials, and tricyclic antidepressants, may cause gum hyperpigmentation as a side effect. Hormonal changes, particularly during pregnancy, can also lead to temporary darkening of the gums.
-
Health Conditions: Some health conditions, such as Addison's disease, Peutz-Jeghers syndrome, and HIV/AIDS, can manifest as dark gums. These conditions affect melanin production or distribution, resulting in hyperpigmentation.
Remedies for Dark Gums:
-
Good Oral Hygiene: Maintaining excellent oral hygiene is essential for healthy gums. Regular brushing, flossing, and using an antiseptic mouthwash can help prevent gum disease and maintain the natural color of your gums.
-
Quit Smoking: Smoking not only contributes to dark gums but also poses significant risks to oral health. Quitting smoking can improve gum health and reduce the likelihood of further gum discoloration.
-
Professional Dental Treatments: If dark gums are a significant concern, seeking professional dental treatments can be beneficial. Procedures such as gum depigmentation, using lasers or chemical agents, can lighten the gum tissue and restore a more uniform color.
Cultural Perspectives on Dark Gums:
Across different cultures, perceptions of beauty and aesthetics can vary widely. In some cultures, such as parts of Africa, Asia, and South America, darker gum color is considered attractive and symbolizes vitality and strength. Conversely, in Western cultures, where pinkish gums are often associated with good oral health, dark gums can be perceived as less desirable. It is important to recognize and appreciate the diversity of beauty standards across cultures, promoting inclusivity and understanding.
Conclusion:
Dark gums, while a natural variation, can sometimes be a cause for concern or self-consciousness. Understanding the causes behind dark gums, including genetics, smoking, medications, and health conditions, is crucial in addressing this issue. By implementing good oral hygiene practices, quitting smoking, and considering professional dental treatments, individuals can effectively manage and potentially lighten dark gums.
Furthermore, embracing cultural perspectives and appreciating the diversity of beauty standards will contribute to a more inclusive and accepting society. Remember, a healthy smile is beautiful, regardless of the color of
Dark Gums How Its Work?
Dark Gums: Understanding the Mechanisms Behind Hyperpigmentation:
Dark gums, or hyperpigmented gums, can be a source of concern for individuals seeking a bright and healthy smile. While the natural color of gums varies among individuals, hyperpigmentation can occur due to various factors. In this article, we will delve into the mechanisms behind dark gums, exploring the role of melanin production, genetics, lifestyle choices, and certain health conditions.
Melanin and Gum Color:
Melanin, the pigment responsible for the color of our skin, hair, and eyes, also plays a role in determining gum color. The amount of melanin present in the gums influences their hue, ranging from pink to darker shades. Melanocytes, specialized cells in the skin and gums, produce and distribute melanin. Factors that affect melanocyte activity can lead to hyperpigmentation or darker gum color.
Genetic Influence:
Genetics can significantly influence gum color. Ethnicity plays a crucial role, as individuals with darker skin tones tend to have higher melanin concentrations in their gums. This is due to genetic factors that control the production and distribution of melanin. Therefore, individuals of African, Asian, or Native American descent are more likely to have naturally darker gums compared to those of European descent.
Lifestyle Choices and Dark Gums:
Certain lifestyle choices can contribute to the darkening of gums:
-
Smoking: Tobacco use, whether through smoking or chewing, is a common cause of gum hyperpigmentation. The chemicals present in tobacco can stimulate the production of melanin and cause it to accumulate in the gum tissue, resulting in darker gums.
-
Oral Hygiene: Poor oral hygiene practices, such as inadequate brushing and flossing, can lead to gum disease and inflammation. Chronic inflammation can trigger an overactive response in melanocytes, causing hyperpigmentation of the gums.
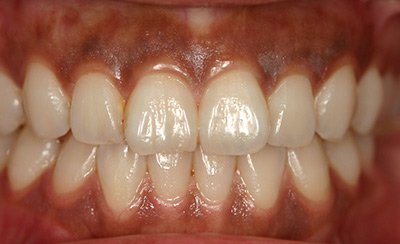
Health Conditions and Dark Gums:
Several health conditions and medications can contribute to dark gums:
-
Hormonal Changes: During pregnancy, hormonal fluctuations can cause an increase in melanin production, leading to temporary gum hyperpigmentation. This condition is commonly referred to as "pregnancy gingivitis."
-
Medications: Some medications, such as minocycline (an antibiotic), antimalarials, and tricyclic antidepressants, have been associated with gum hyperpigmentation as a side effect. These drugs can affect melanocyte activity and cause melanin accumulation in the gums.
-
Underlying Health Conditions: Certain medical conditions, including Addison's disease, Peutz-Jeghers syndrome, and HIV/AIDS, can cause dark gums. These conditions disrupt melanin production or distribution, resulting in hyperpigmentation.
Conclusion:
Dark gums, or hyperpigmented gums, can be influenced by various factors, including melanin production, genetics, lifestyle choices, and certain health conditions. Understanding the mechanisms behind dark gums is crucial in addressing concerns and seeking appropriate treatment options. While some individuals embrace the natural variation in gum color, others may opt for professional dental treatments, such as gum depigmentation, to lighten the gums. Maintaining good oral hygiene, avoiding tobacco use, and being aware of any underlying health conditions are essential in promoting healthy gums and overall oral well-being. Remember, consulting with a dental professional is advisable for personalized guidance and treatment options related to dark gums.


