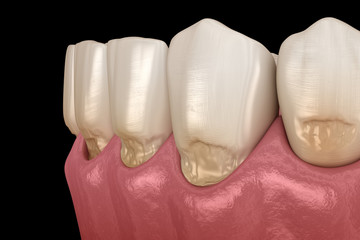
Gingival Depigmentation
Gingival Depigmentation, also known as gum bleaching, is a cosmetic dental procedure that aims to remove or reduce the dark pigmentation on the gums. While pigmented gums are considered normal and pose no health risks, some individuals may seek depigmentation for aesthetic purposes or due to self-consciousness about the appearance of their gums.
What IS Gingival Depigmentation:
Gingival Depigmentation This article provides an overview of gingival depigmentation, including its causes, procedures, and important considerations for individuals considering this treatment.
Causes of Gingival Pigmentation:
Gingival pigmentation occurs due to an increased deposition of melanin, the pigment responsible for the color of our skin, hair, and eyes, in the gum tissue. There are several factors that can contribute to the development of pigmented gums:
- Ethnicity: People with darker skin tones, such as individuals of African, Asian, or Mediterranean descent, are more prone to gingival pigmentation. This is because individuals with darker skin produce higher levels of melanin.
- Hormonal changes: Hormonal imbalances, such as those occurring during puberty, pregnancy, or while taking certain medications, can lead to an increase in melanin production, resulting in pigmented gums.
- Smoking: The habit of smoking has been linked to gingival pigmentation. The chemicals present in tobacco smoke can stimulate the production of melanin, leading to darker gums.
Gingival Depigmentation Procedures:
There are three main procedures commonly used for gingival depigmentation:
- Surgical Depigmentation: This procedure involves removing the pigmented epithelial layer of the gums. The dentist or periodontist uses a scalpel, laser, or electrosurgical instruments to carefully remove the outer layer, revealing the lighter tissue beneath. This method is usually performed under local anesthesia.
- Chemical Depigmentation: In this procedure, a chemical agent, typically a 20-30% solution of hydrogen peroxide, is applied to the pigmented gums. The chemical acts as a bleaching agent, lightening the color of the gums. Multiple applications may be required to achieve the desired results.
- Laser Depigmentation: Laser technology is another option for gingival depigmentation. A dental laser is used to remove the pigmented layer of the gums. Laser treatment offers several advantages, including precise control, minimal bleeding, reduced discomfort, and faster healing compared to traditional surgical methods.
Important Considerations:
Before undergoing gingival depigmentation, individuals should consider the following factors:
Consultation:
It is crucial to consult with a qualified dentist or periodontist to assess the suitability of the procedure for your specific case. They will evaluate your gum health, discuss your expectations, and provide recommendations based on your individual circumstances.
- Potential Risks: While gingival depigmentation is generally safe, it can carry certain risks like infection, post-operative discomfort, bleeding, or gum recession. Your dentist will discuss these risks with you and provide the necessary precautions to minimize any adverse effects.
- Maintenance: After undergoing depigmentation, it is essential to maintain good oral hygiene practices and follow the dentist's instructions for proper care. Regular dental visits and professional cleanings will help keep your gums healthy and maintain the results of the procedure.
- Realistic Expectations: It is important to have realistic expectations regarding the outcome of gingival depigmentation. While the procedure can significantly lighten the gum color, complete removal of pigmentation may not always be achievable. Your dentist will explain the expected outcomes based on your individual situation.
Conclusion:
Gingival depigmentation offers a solution for individuals seeking to reduce or eliminate dark pigmentation on their gums. By understanding the causes, available procedures, and important
Gingival Depigmentation How Its Work?
Gingival depigmentation, also known as gum bleaching, is a cosmetic dental procedure aimed at removing or reducing the dark pigmentation on the gums. The process involves several techniques that work to lighten the color of the gum tissue. Here's how gingival depigmentation works:
Surgical Depigmentation:
Surgical depigmentation is one of the most common methods used for gingival depigmentation. It involves the physical removal of the pigmented layer of gum tissue. Here's how the procedure typically works:
a. Anesthesia: Before the procedure begins, the dentist or periodontist administers a local anesthetic to numb the gums. This ensures that the patient does not experience any pain or discomfort during the process.
b. Preparation: Once the area is numbed, the dentist or periodontist uses a scalpel, laser, or electrosurgical instruments to carefully remove the outer layer of pigmented gum tissue. This process reveals the lighter tissue underneath.
c. Healing: After the pigmented tissue is removed, the gums are left to heal naturally. The healing process usually takes a few weeks, during which the gums regenerate and develop a lighter appearance.
Chemical Depigmentation:
Chemical depigmentation is another method used to lighten pigmented gums. It involves the application of a chemical agent to bleach the gum tissue. Here's how the procedure typically works:
a. Assessment: Before the procedure, the dentist or periodontist assesses the patient's gum health and determines the appropriate concentration of the chemical agent.
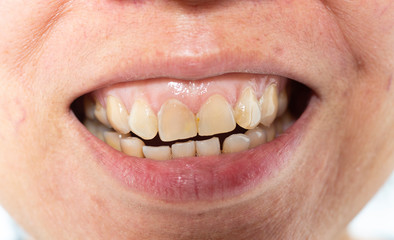
b. Application: The selected chemical agent, commonly a 20-30% solution of hydrogen peroxide, is applied to the pigmented gums. The chemical works as a bleaching agent, lightening the color of the gum tissue.
c. Multiple Sessions: Depending on the severity of pigmentation, multiple applications of the chemical agent may be required to achieve the desired results. Each session is typically spaced out to allow for healing between treatments.
Laser Depigmentation:
Laser depigmentation is a modern and minimally invasive technique used for gingival depigmentation. It utilizes laser technology to remove pigmented gum tissue. Here's how the procedure typically works:
a. Anesthesia: The gums are numbed using a local anesthetic to ensure a pain-free experience for the patient.
b. Laser Treatment: A dental laser is used to precisely remove the pigmented layer of the gums. The laser energy selectively targets and vaporizes the melanin pigment, resulting in a lighter gum color.
c. Benefits: Laser depigmentation offers several advantages, including minimal bleeding, reduced discomfort, faster healing, and precise control over the treatment area.
Final Words:
It's important to note that the choice of technique may vary depending on the individual's specific case and the expertise of the dentist or periodontist performing the procedure. Proper consultation with a qualified dental professional is crucial to determine the most suitable method for gingival depigmentation.


