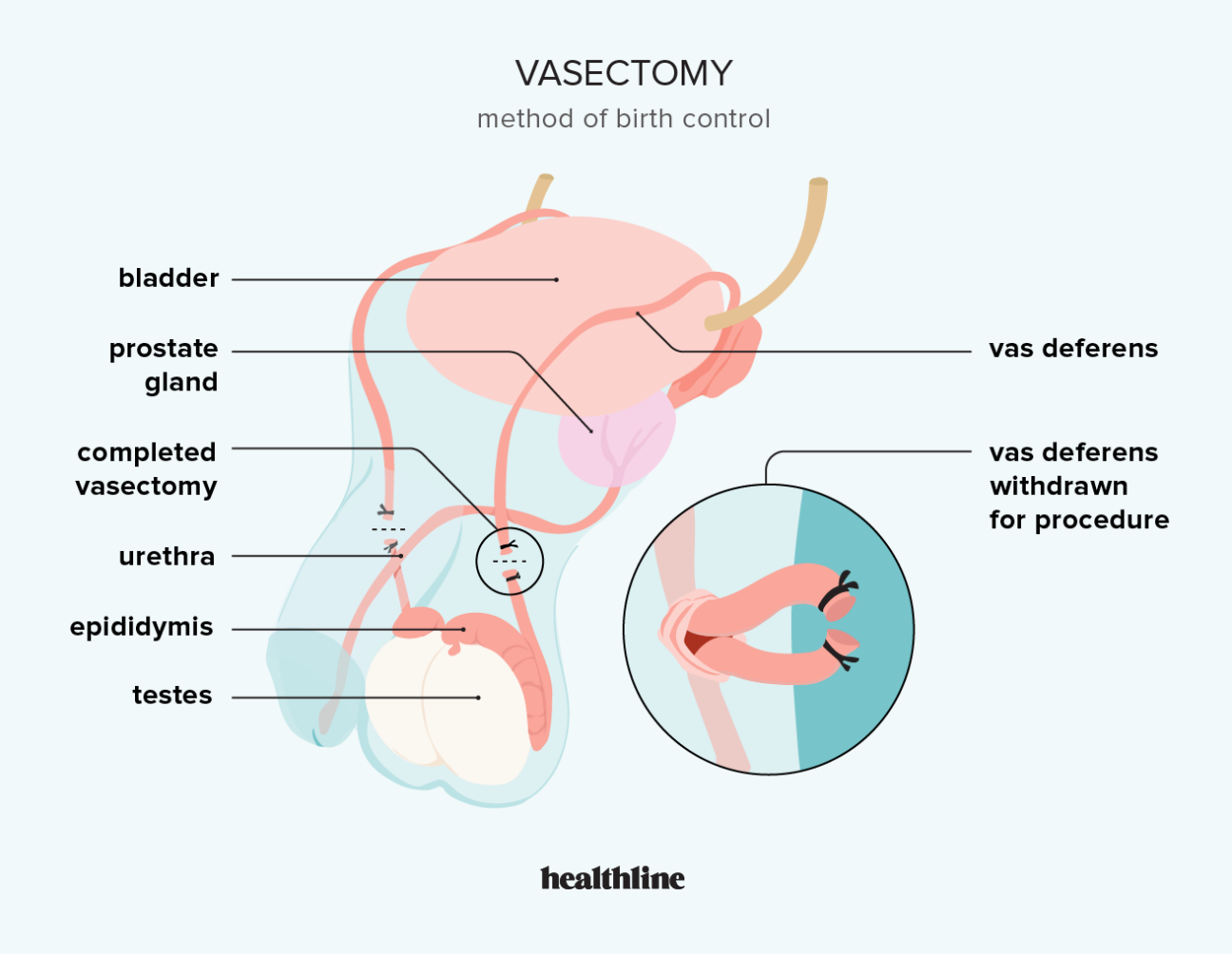
Vasectomy is a medical procedure that involves the surgical removal or blocking of the vas deferens, which is the tube that carries sperm from the testicles to the penis. It is a form of permanent birth control that is popular among men who have decided that they no longer want to have children. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of vasectomy, including its benefits, risks, and how it is performed.
What is Vasectomy?
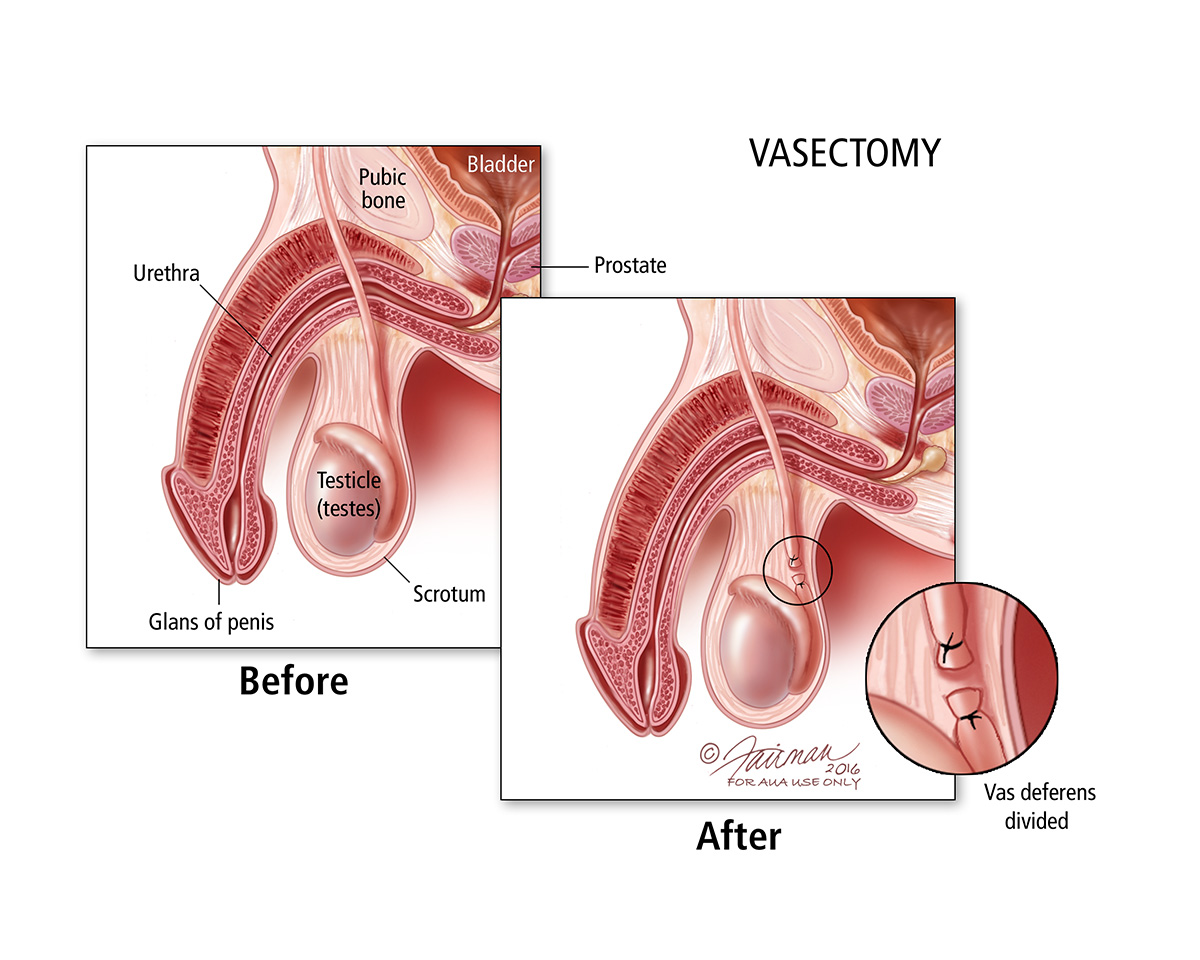
Vasectomy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that is performed on an outpatient basis. During the procedure, a urologist or a specialized doctor will make a small incision in the scrotum and access the vas deferens. The vas deferens will then be cut, tied, or sealed using various methods, preventing sperm from reaching the semen. Vasectomy does not affect a man's ability to ejaculate, nor does it affect his sex drive or hormone levels.
Benefits of Vasectomy:
One of the main benefits of vasectomy is that it is a highly effective form of birth control. After the procedure, sperm are no longer present in a man's semen, which means that he cannot impregnate his partner. Vasectomy is also a permanent form of birth control, which means that men who have had the procedure can enjoy sexual intimacy without worrying about unintended pregnancies.
Another benefit of vasectomy is that it is a simple, safe, and relatively painless procedure. The procedure can be performed in a doctor's office, usually takes less than 30 minutes, and does not require general anesthesia. Most men can resume their normal activities within a few days after the procedure, and there is a very low risk of complications or side effects.
Risks of Vasectomy:
Although vasectomy is a safe and effective procedure, there are some risks associated with it. The most common risk is that of post-operative pain, swelling, and bruising. These symptoms are usually mild and can be managed with pain medication, ice packs, and rest. In rare cases, however, more serious complications can occur, such as infection, bleeding, or damage to surrounding tissue.
Another potential risk of vasectomy is that it may not be immediately effective. After the procedure, men must continue to use contraception until their semen has been tested and confirmed to be free of sperm. This usually takes around three months, and failure to wait for confirmation can result in unintended pregnancy.
How is Vasectomy Performed?
Vasectomy is typically performed under local anesthesia, which means that the patient is awake but numb during the procedure. The doctor will begin by making a small incision in the scrotum, then locate and expose the vas deferens. The vas deferens is then cut, tied, or sealed using various methods, depending on the doctor's preference. Once the procedure is complete, the incision is closed with stitches or surgical glue.
After the procedure, men will need to rest for a few days and avoid strenuous physical activity. They should also apply ice packs to the scrotum to reduce swelling and take pain medication as prescribed. Most men can return to work within a week, although they should avoid sexual activity for at least a week after the procedure.
Conclusion:
Vasectomy is a safe and effective form of permanent birth control that is becoming increasingly popular among men. It is a simple, minimally invasive procedure that can be performed on an outpatient basis and offers numerous benefits, including highly effective contraception and a low risk of complications. As with any medical procedure, however, there are some risks associated with vasectomy, and men should discuss the procedure thoroughly with their doctor before making a decision.
Vasectomy How Its Work?
Vasectomy is a form of permanent birth control for men that involves the surgical removal or blocking of the vas deferens, the tube that carries sperm from the testicles to the penis. By blocking the vas deferens, the sperm are prevented from entering the semen, which means that a man cannot impregnate his partner.
During the procedure, a urologist or specialized doctor will make a small incision in the scrotum, usually on both sides, and access the vas deferens. The vas deferens is then cut, tied, or sealed using various methods, depending on the doctor's preference. Once the vas deferens is blocked, sperm can no longer mix with the semen, and a man's ejaculate will no longer contain sperm.
There are two main types of vasectomy procedures:
traditional vasectomy and the no-scalpel vasectomy. The traditional vasectomy involves making two small incisions in the scrotum, whereas the no-scalpel vasectomy involves making a single puncture hole. Both procedures are highly effective and have a low risk of complications.
Vasectomy is typically performed under local anesthesia, which means that the patient is awake but numb during the procedure. The entire procedure usually takes less than 30 minutes, and most men can return to their normal activities within a few days.
After the procedure, men will need to rest for a few days and avoid strenuous physical activity. They should also apply ice packs to the scrotum to reduce swelling and take pain medication as prescribed. It is important to note that vasectomy does not offer immediate protection against pregnancy, and men will need to continue using contraception until their semen has been tested and confirmed to be free of sperm. This usually takes around three months, and failure to wait for confirmation can result in unintended pregnancy.
If you want to get amazing benefits by using this link
Conclusion:
Overall, vasectomy is a safe and effective form of permanent birth control that offers numerous benefits to men who have decided that they no longer want to have children. Men who are considering vasectomy should discuss the procedure thoroughly with their doctor and carefully weigh the benefits and risks before making a decision.


