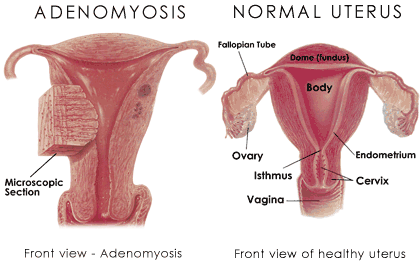
Adenomyosis is a condition that affects many women worldwide, yet it often remains underdiagnosed and misunderstood. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of adenomyosis, exploring its causes, symptoms, and available treatment options.
What is Adenomyosis?
Adenomyosis is a medical condition characterized by the presence of endometrial tissue, which normally lines the uterus, growing into the muscular wall of the uterus. This can result in a variety of symptoms and complications for affected individuals.
Causes of Adenomyosis:
While the exact cause of adenomyosis remains unclear, several factors may contribute to its development. These include hormonal imbalances, prior uterine surgeries, inflammation, and genetic predisposition. Additionally, women who have given birth multiple times or are in their late 30s to 40s are at higher risk of developing adenomyosis.
Symptoms of Adenomyosis:
The symptoms of adenomyosis can vary in severity from mild discomfort to debilitating pain. Common symptoms include:
-
Menstrual cramps: Women with adenomyosis often experience severe menstrual cramps that may worsen over time.
-
Heavy menstrual bleeding: Adenomyosis can lead to heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding, resulting in anemia in some cases.
-
Pelvic pain: Chronic pelvic pain, particularly during menstruation or intercourse, is a hallmark symptom of adenomyosis.
-
Enlarged uterus: In advanced cases, the uterus may become enlarged and tender to the touch.
Diagnosis of Adenomyosis:
Diagnosing adenomyosis can be challenging due to its similarity to other gynecological conditions such as endometriosis and fibroids. However, several diagnostic tools can aid in identifying adenomyosis, including transvaginal ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and, in some cases, diagnostic laparoscopy.
Treatment Options:
Treatment for adenomyosis aims to alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life. Depending on the severity of symptoms and individual preferences, treatment options may include:
-
Pain management: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or prescription medications may help manage menstrual pain associated with adenomyosis.
-
Hormonal therapy: Birth control pills, hormonal IUDs, or other hormonal medications can help regulate menstrual cycles and reduce symptoms.
-
Uterine artery embolization (UAE): This minimally invasive procedure involves blocking the blood supply to the uterus, effectively shrinking adenomyosis lesions and reducing symptoms.
-
Hysterectomy: In severe cases where other treatments have failed or if the patient has completed childbearing, a hysterectomy may be recommended as a definitive treatment for adenomyosis.
Conclusion:
Adenomyosis is a common yet often overlooked gynecological condition that can significantly impact a woman's quality of life. By understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals affected by adenomyosis can make informed decisions about their healthcare and seek appropriate medical guidance. If you suspect you may have adenomyosis or are experiencing symptoms related to this condition, consult with a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and management.